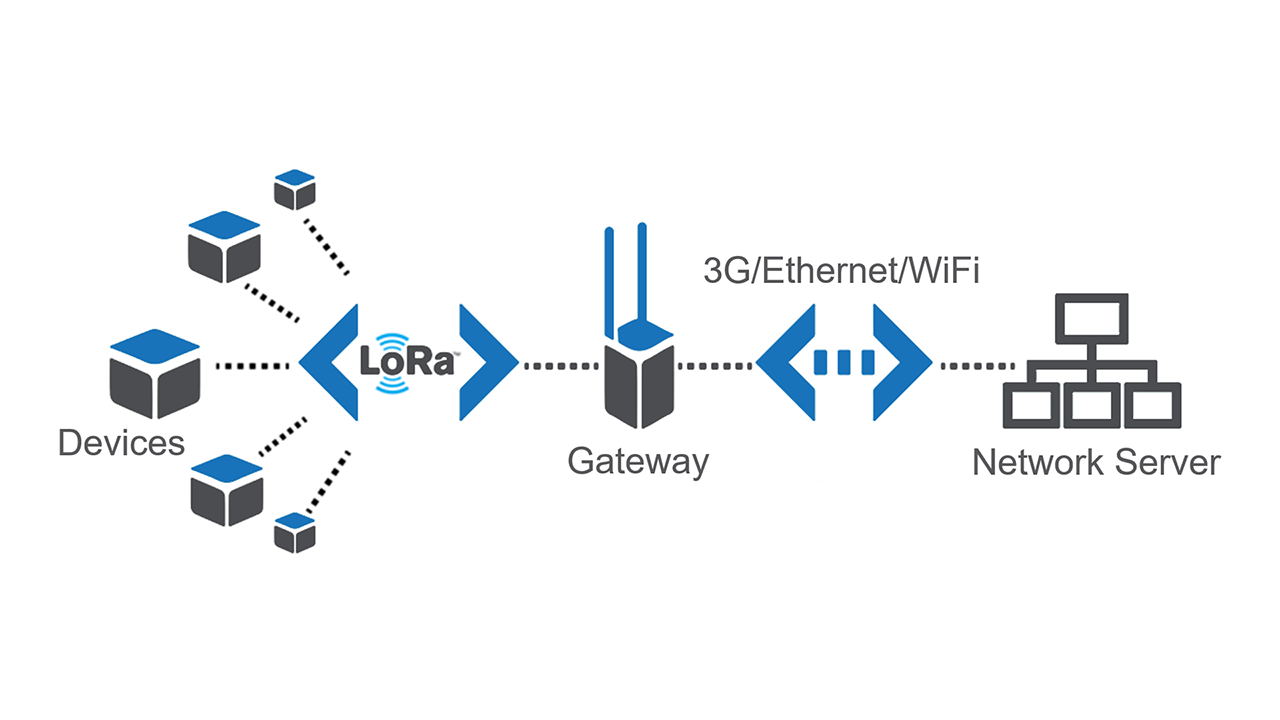
The IoT is going to connect the world. That’s how
it’s stated in the introduction video of the LoRa Alliance, an association
devoted to the large scale deployment of LPWAN through the placing in service
the LoRaWAN open standard.
APPLICATION OF
LORAWAN AND WI-FI IN IOT
Approaching a large
proportion of IoT use cases, LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi still serve different purposes
in IoT. Today Wi-Fi is most often deployed to support critical IoT use cases
whereas LoRaWAN is used for massive IoT use cases.
Massive IoT is
applied to connect billions of battery-powered objects, transmit a low amount
of data at a low data rate and optimize energy consumption. The application of
massive IoT may be found in cities, agriculture, logistics, buildings
(airports, hotels, stadiums, multi-dwelling units, homes, venues, etc.), and
supply chain or transportation.
Critical IoT serves
as a connection of millions of objects, communication between a massive amount
of data with low latency and high reliability at a higher data rate, which
mostly results in higher power consumption. The applications are found in
transportation (connected vehicle, traffic control), smart health (surgery,
patient monitoring), and industry (real-time applications, robots, remote
manufacturing).
HYBRID WI-FI/LORAWAN USE CASES
For decades, LoRaWAN and Wi-Fi technologies were applied for
daily services such as smart buildings, cities, and venues, the same as
automotive and smart transportation and location services. The impressive
growth of new wireless technologies enabled new commercial use cases in the following
commercial sectors.
SMART BUILDINGS
In the case of smart buildings, Wi-Fi was commonly used for
high-speed Internet surfing, broadband services, and security cameras. LoRaWAN,
in contrast, served the leak and smoke detection, air conditioning, door/window
opening alarms, asset and vehicle tracking, room energy monitoring and more.
The alliance of these two technologies creates the
possibility of on-demand streaming for battery-powered devices. For example,
low power LoRaWAN sensors can activate the device that transmits information to
the cloud (using Wi-Fi technology) only when it detects sound, motion or
vibration in the building. Therefore, the battery of the device will be
preserved from unnecessary usage.
PLACES OF RESIDENCE AND VENUES
Billions of personal and professional devices in homes use
Wi-Fi to provide instant connection, whereas LoRaWAN is used for traffic light
monitoring, waste management, and traffic direction. It is suggested to use
LoRaWAN picos for handling Wi-Fi backhaul portion of the network to the user
set-top box to expand coverage of home services to the neighborhood. In such a
way, these “neighborhood IoT networks” may endorse the support of new
geolocation services and provide the basis for the demand-response services.
TRANSPORTATION
Currently, Wi-Fi is used for passenger entertainment and access control, while LoRaWAN is used for fleet tracking and vehicle maintenance. Hybrid use cases identified in the paper include location and video streaming. Automotive and smart transportation companies could combine Wi-Fi and LoRaWAN to make location and video streaming more reliable on busses, planes, and other mass transit services.















